The Injury You Build Quietly: Micro-Trauma Accumulation
Series EP.4 — MADI-BONE CLINIC | Gangnam (Seolleung Station)
Previously in This Series
What “Micro-Trauma Accumulation” Means
Micro-trauma accumulation is the gradual build-up of microscopic tissue damage when repetitive load exceeds current tissue capacity and recovery isn’t sufficient.
It explains why office workers develop tech neck (forward head posture, FHP) and why athletes get tendinopathy (e.g., tennis/golfer’s elbow) even without a single dramatic injury.
The concept integrates well with the tendon continuum model—tissues progress from reactive changes to disrepair and degeneration if load errors persist.
Cook & Purdam 2009;
Cook et al. 2016 update.
Two Everyday Examples
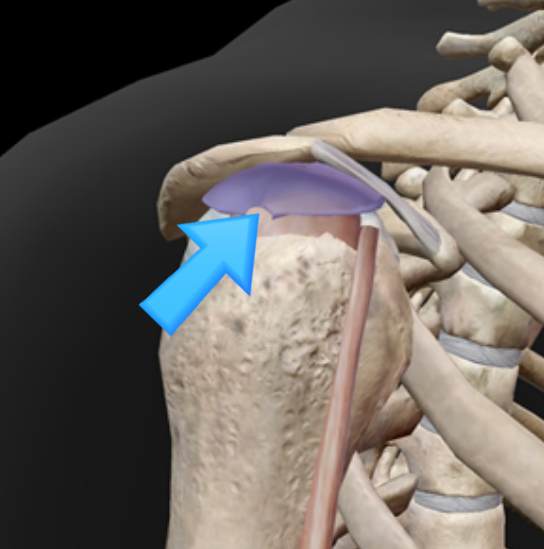
1) Tech Neck in Desk Workers
Prolonged screen time and phone use are associated with greater neck pain risk in a dose–response manner—more hours, higher risk.
BMC Public Health 2025.
Head-forward posture increases upper trapezius and neck muscle activation, adding cumulative load.
Lee et al. 2015.
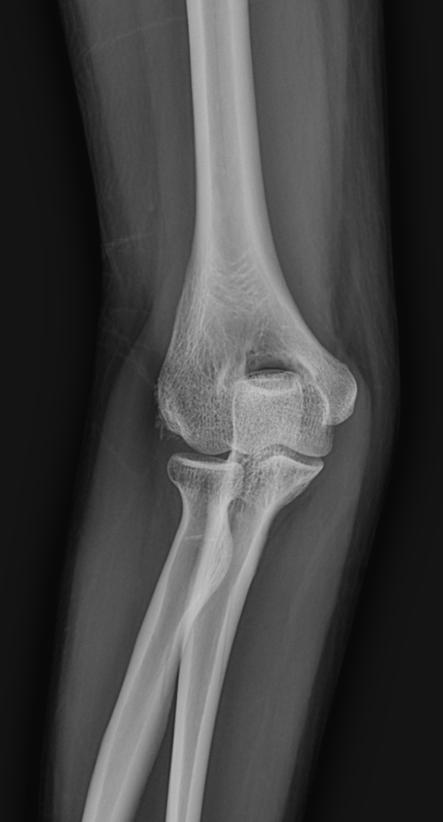
2) Elbow Tendinopathy in Racket Sports
Repeated gripping, wrist extension/flexion and load spikes can push the extensor/flexor tendon units along the tendinopathy continuum.
Management is not only about pain relief—it’s about capacity building with eccentric or heavy-slow resistance and minimizing ill-timed load spikes.
Coombes et al., BMJ 2010.
Load vs Capacity: The Practical Model
- Capacity: what your tissue can currently tolerate (varies by sleep, age, past injury, strength).
- Load: the stress you apply (volume × intensity × frequency × mechanics).
- Mismatch: injury risk rises when load increases too fast for your capacity.
In sport science, sudden load spikes are a consistent risk factor—“train smarter, not just more.”
Gabbett 2016.
How We Intervene (Clinic Playbook)
- Deload the aggravating pattern (reduce volume/intensity/frequency; adjust mechanics/equipment).
- Calm pain to enable training (short NSAIDs when indicated; manual therapy; situational bracing/strap).
Corticosteroid injection helps short-term but has higher long-term recurrence; use selectively.
Bisset et al., 2006 RCT. - Rebuild capacity with eccentric or heavy-slow resistance (wrist extensor/flexor for elbow; deep neck flexor + scapular endurance for FHP).
BMJ 2010 review. - Ergonomics & micro-breaks for desk work; progressive return-to-sport for athletes.
- Optionals: ESWT can be considered in chronic tendinopathy (evidence mixed; consider with loading programs).
Wang 2012 review;
Romeo 2014 review.
Self-Check & Early Warning Signs
- Desk: you’ve added hours of phone/computer time recently and neck tightness escalates by late afternoon.
- Sport: you increased hitting volume or changed equipment/grip, and elbow pain appears during/after sessions.
- Both: symptoms fade with a few days’ deload but return when you resume at the same volume—classic micro-trauma pattern.
Action Plan You Can Start Today
- For tech neck: monitor top ≈ eye level; timer every 30–40 min; chin-tuck 6×8s; scapular retraction 10 reps; thoracic extension 10 reps.
- For elbow: pause aggravating drills 3–5 days; begin eccentrics (3–5 s lowering; 12–15 reps × 2–3 sets); forearm stretch 30–40 s × 2–3; review grip size/technique.
- Progress gradually: increase weekly volume by ~10–20% only if symptoms are stable or improving.
MADI-BONE CLINIC (Seolleung Station, ~3 min on foot)
MADI-BONE CLINIC
3F, 428 Seolleung-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul
Seolleung Station (Line 2), Exit 1 — ~3 minutes on foot
02-736-2626
⏰ Mon–Fri 09:30–18:30 / Sat 09:30–13:00 (Closed Sundays & Public Holidays)
Sources
- Cook JL, Purdam CR. Is tendon pathology a continuum? Br J Sports Med. 2009 & Revisiting the continuum 2016.
- Gabbett TJ. The training–injury prevention paradox. Br J Sports Med. 2016.
- Coombes BK, et al. Lateral epicondylalgia — epidemiology, pathophysiology & management. BMJ. 2010.
- Bisset L, et al. Mobilisation/exercise vs corticosteroid injection. RCT. 2006.
- Lee KJ, et al. FHP increases neck muscle activation. 2015.
- Meng Y, et al. Sedentary behaviour & neck pain, systematic review/meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. 2025.
- Wang CJ. ESWT in musculoskeletal disorders. 2012; Romeo P. ESWT & tissue regeneration. 2014.
This article is educational and does not replace an individual medical evaluation or treatment plan.